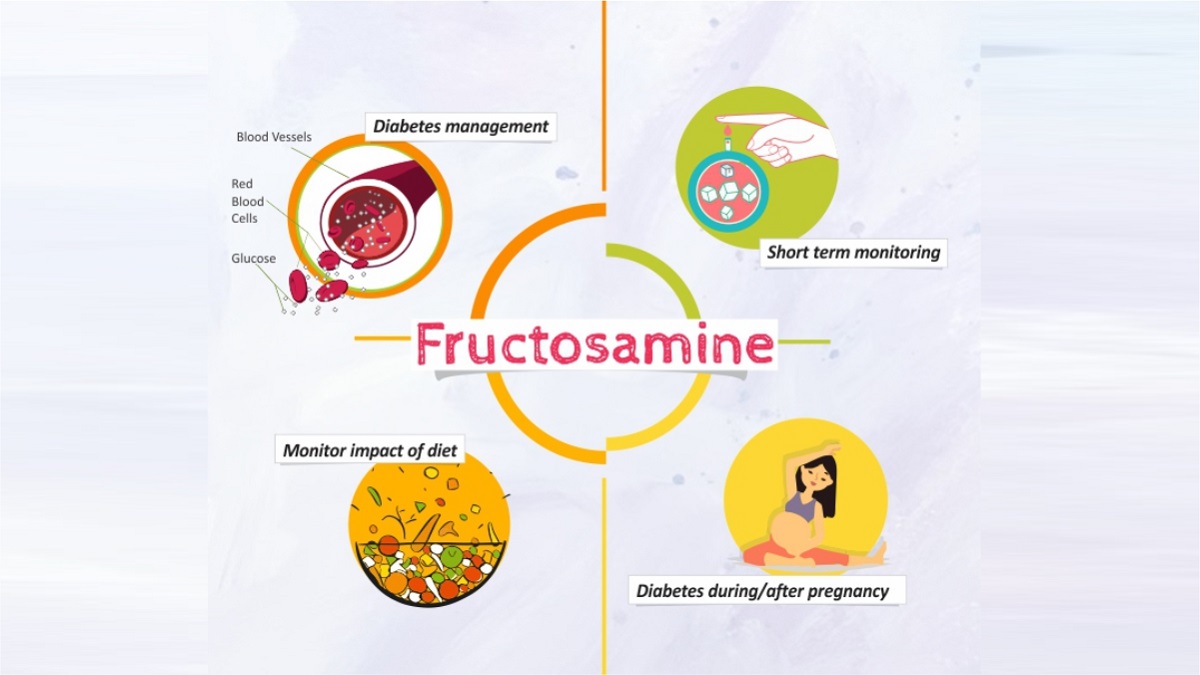
This test measures the total amount of fructosamine (glycated protein) in the blood. The test is used to help monitor your blood glucose level over short, to help determine the effectiveness of changes to your diabetic treatment plan.
Fructosamine is a compound that is formed when glucose combines with protein.
Glucose molecules will permanently combine with proteins in the blood in a process called glycation.
The more glucose that is present in the blood, the greater the amount of glycated proteins that are formed.
These combined molecules persist for as long as the protein is present in the blood.
Serum proteins are present in the blood for a shorter time, about 14 to 21 days,
so glycated proteins, and the fructosamine test, reflect average glucose levels over 2 to 3 weeks.
Instances where fructosamine may be considered over HBA1c include:
Rapid changes in diabetes treatment.
Diabetic pregnancy
Shortened Red Blood Cells lifespan.
The presence of some hemoglobin variants, such as hemoglobin S in sickle cell anemia, may affect certain methods for measuring A1c.
What does the test result mean?
A high fructosamine level means that the average blood glucose over the previous 2 to 3 weeks has been elevated.
A normal fructosamine level may indicate good glucose control and that the current treatment plan is effective for the individual.
Falsely low fructosamine results may be seen with decreased blood total protein and/or albumin levels.
Keeping blood glucose levels as close as possible to normal helps individuals with diabetes to avoid many of the complications and progressive damage associated with elevated glucose levels.



